We've been eyeing the Armenian market for the past two years.
In fact, we almost took off two years ago but decided to pause our activities. Now, with updated policies and a clearer economic landscape, it's time to reassess the opportunities Armenia offers, especially in the IT sector.
Exploring the Best of Armenia: A Travel Video from our Business Trip
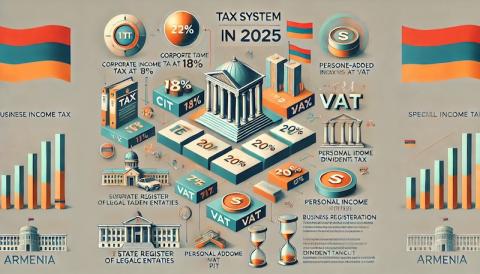
Overview of the Armenian Tax System in 2025
Armenia has positioned itself as an attractive destination for businesses with its simplified and competitive tax system. The primary taxes companies need to consider include:
- Corporate Income Tax (CIT): Currently set at 18%, with potential reductions for certain industries, including IT and innovation-focused sectors.
- Value Added Tax (VAT): A standard 20% rate applies, but companies with annual revenue below a specific threshold (currently AMD 115 million) are exempt.
- Personal Income Tax (PIT): A flat rate of 20%, applicable to both residents and non-residents.
- Dividend Tax: 5% for both residents and non-residents.
- Microbusiness Regime: Companies earning under AMD 24 million annually may qualify for tax exemptions.
Registering a Company in Armenia
The process of registering a business in Armenia has been streamlined to attract foreign investment. Key steps include:
- Choosing a Legal Structure: Most IT companies opt for an LLC (Limited Liability Company), offering limited liability and flexibility.
- Company Registration: This involves submitting an application to the State Register of Legal Entities, which can typically be done within a few business days.
- Obtaining a Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN): Issued by the tax authorities upon registration.
- Opening a Corporate Bank Account: Required for financial operations.
- Compliance with Regulatory Requirements: IT companies may also need to register with the Ministry of High-Tech Industry.
Special Economic Zones (SEZs)
Armenia offers Special Economic Zones (SEZs) aimed at attracting foreign investment with additional benefits, such as:
- Tax Incentives: Companies operating within SEZs can benefit from exemptions on corporate income tax, VAT, and customs duties.
- Customs Privileges: Duty-free import and export of goods within the SEZs.
- Simplified Regulations: Streamlined processes for business operations and reduced administrative burdens.
- Infrastructure Support: Access to modern facilities, logistics, and business services tailored to specific industries, including IT and manufacturing.
Special Benefits for IT Companies
Armenia offers several incentives for IT firms, including:
- Tax Exemptions: Startups may benefit from zero corporate tax and reduced payroll taxes for up to five years under government support programs.
- Grants and Subsidies: Various government and international programs provide funding opportunities for innovation and development.
- Talent Pool: A growing workforce with competitive salaries compared to Western markets.
Challenges to Consider
While Armenia presents many advantages, there are challenges, such as:
- Bureaucratic Hurdles: Despite improvements, navigating regulations can still be time-consuming.
- Currency Fluctuations: The Armenian dram (AMD) can be volatile, affecting financial planning.
- Political Stability: Regional tensions may impact business operations.
Conclusion
As we reconsider our expansion into Armenia, it's clear that the country offers substantial benefits, particularly for IT businesses. However, a careful assessment of the regulatory and economic landscape is essential. The tax system is attractive, but operational challenges remain.
For those considering the Armenian market, the key takeaway is simple: understand the tax benefits, stay informed about regulatory updates, and leverage available incentives to maximize your investment potential.